Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Benin (BN). This page lets you explore Benin and its border countries (Country Location: Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Benin, between Nigeria and Togo) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Benin, Africa, starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Benin in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Benin, a nation in West Africa, boasts a rich cultural and historical heritage. The country is home to various ethnic groups, including the Yoruba, Dendi, Bariba, Fula, and others, each contributing to its diverse cultural tapestry. The Kingdom of Dahomey, a regional power in the 18th and 19th centuries, is a notable part of Benin’s history. The kingdom was known for its organized economy, military, and involvement in the Atlantic slave trade. In the late 19th century, France began to control Dahomey’s coastal areas, leading to its full conquest by 1894. Benin achieved independence from France in 1960 and underwent several political transformations, moving from Marxist-Leninist principles to a representative government in 1989. Today, it is a presidential republic, with Patrice Talon serving as president since 2016.
Overview
Situated in Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Benin, between Nigeria and Togo, Benin covers an area slightly smaller than Pennsylvania, totaling 112,622 sq km. The country’s climate is tropical, with a hot, humid south and a semiarid north. Its geography includes mostly flat to undulating plains with some hills and low mountains. Benin’s economy is diverse, featuring small offshore oil deposits, limestone, marble, timber, and a strong agricultural sector. The population of approximately 14.2 million (2023) enjoys a rich tapestry of cultures and languages, with French being the official language.
Official Name: Republic of Benin
Date of Formation: 1 August 1960 (from France)
Capital: Porto-Novo (constitutional capital); Cotonou (seat of government)
Population: 14,219,908 (2023 est.)
Total Area: 43,484 Sq. Miles / 112,622 Sq. Km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: French (official), Fon, and Yom, along with other indigenous languages
Religions: Muslim 27.7%, Roman Catholic 25.5%, Protestant 13.5%, Vodoun 11.6%, other Christian 9.5%, other traditional religions 2.6%, other 2.6%, none 5.8% (2013 estimate)
Ethnic Origin: Fon and related 38.4%, Adja and related 15.1%, Yoruba and related 12%, Bariba and related 9.6%, Fulani and related 8.6%, Ottamari and related 6.1%, Yoa-Lokpa and related 4.3%, Dendi and related 2.9%, other 0.9%, foreigner 1.9% (2013 estimate)
Government: Presidential republic
Currency: West African CFA franc (XOF)
Literacy Rate: 45.8% (2021 estimate)
Calorie Consumption: N/A
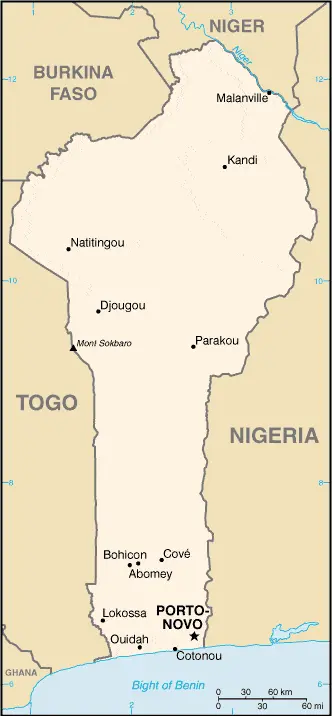
Benin Google Maps
Google Maps provides detailed geographic information for Benin, facilitating navigation and exploration of its diverse regions. From the bustling markets of Cotonou to the historic palaces of Abomey, Google Maps is an indispensable tool for travelers and locals alike.
Benin stretches north from the West African coast. In 1990, Benin became one of the pioneers of African democratization, ending 17 years of one-party Marxist-Leninist rule. Sandy coastal region. Numerous lagoons lie just behind the shoreline. Forested plateaus inland. Mountains in the northwest.
The map below shows Benin with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google map above shows Benin with its location: Africa (geographic coordinates: 9 30 N, 2 15 E) and the international borders of Benin; total: 2,123 km. Border countries (total: 4): Burkina Faso 386 km, Niger 277 km, Nigeria 809 km, Togo 651 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Benin, Africa, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warranted given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Benin Google map and facts/wiki.
Climate
Benin, located in West Africa, exhibits a tropical climate that greatly influences its ecological system, agricultural practices, and daily life. Distinct regional variations, with a hot and humid south and a semiarid north, characterize the climate.
- North-South Climatic Variation: In the southern part of Benin, the climate is typically hot and humid, with two rainy and two dry seasons. The main rainy season lasts from April to July, followed by a shorter and less intense rainy period from September to November. The dry seasons occur from December to March and in August. The southern region’s proximity to the equator accounts for its high humidity levels and more consistent rainfall.
- Semiarid North: Conversely, the northern part of Benin experiences a semiarid climate, characteristic of the Sahel region of Africa. This area has one rainy season from May to September, followed by a long, dry season from October to April. The rainfall is less predictable and often insufficient, impacting agriculture and water availability in this region.
- Seasonal Temperature Variations: Across Benin, temperatures vary seasonally. The southern region generally maintains warmer temperatures year-round, with averages ranging from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F). In contrast, the northern region can experience more extreme temperatures, with daytime highs reaching up to 40°C (104°F) during the hot season before the onset of the rains.
- Harmattan Winds: A significant climatic feature in northern Benin is the Harmattan, a dry and dusty northeasterly trade wind. This wind blows from the Sahara Desert into the region between November and March, significantly lowering humidity and sometimes obstructing visibility due to dust.
- Impact on Agriculture: The varying climatic conditions across Benin heavily influence agricultural activities. With its two rainy seasons, the south is conducive to growing various crops, including corn, cassava, and yams. In the north, the single, shorter rainy season restricts farming activities to this period, with millet and sorghum being the predominant crops.
- Climate Change Challenges: Like many countries, Benin faces challenges related to climate change. These include increased variability in rainfall patterns and more frequent extreme weather events like droughts and floods. Such changes pose risks to food security, water resources, and the overall livelihood of the population.
- Coastal Region Vulnerability: The coastal areas of Benin are particularly vulnerable to climate change, experiencing issues like coastal erosion and rising sea levels. This affects the local ecosystems and has implications for these regions’ human settlements and economic activities.
In summary, with its regional variations from a hot and humid south to a semiarid north, Benin’s tropical climate significantly impacts the nation’s agricultural practices, lifestyle, and environmental challenges. Seasonal variations in rainfall and temperature, along with phenomena like the Harmattan winds, define the unique climatic characteristics of this West African nation. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns, Benin faces ongoing challenges adapting to these environmental changes.
Geography
Benin’s geography is marked by a diverse landscape that ranges from flat plains to rolling hills and low mountains, encompassing a variety of ecosystems that contribute to the country’s natural and cultural richness.
- Terrain and Topography: Most of Benin’s terrain is characterized by flat to undulating plains, particularly in the southern regions. These plains gradually rise into hills and low mountains as one moves northward. The highest point in the country, an unnamed elevation near Kotopounga, stands at 675 meters (2,215 feet) and is located in the Atakora Range in the northwest. This area is known for its scenic beauty and is significantly different from the flat coastal areas.
- Coastline and Marine Geography: Benin has a relatively short coastline, stretching approximately 121 kilometers (75 miles) along the Bight of Benin. This coastline is known for its sandy beaches and is an important part of the country’s geography, impacting its climate, economy, and cultural life. The coastal area is also subject to erosion and rising sea levels, posing environmental challenges.
- Rivers and Water Systems: The country is crisscrossed by several rivers, the most significant being the Oueme River, which flows southwards into the Atlantic Ocean. These rivers are vital for agriculture, providing essential water sources for irrigation and supporting local ecosystems.
- Forest Cover and Biodiversity: Benin’s landscape includes significant forest cover, especially in the north and central regions. These forests are home to diverse flora and fauna, contributing to the country’s biodiversity. The Pendjari National Park in the northwest is one of the key biodiversity areas, offering habitat to a variety of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and various species of birds.
- Surrounding Countries: Benin is bordered by four countries. To the west lies Togo, with a shared border of about 651 kilometers (404 miles). On its eastern border, it neighbors Nigeria, with a border length of approximately 809 kilometers (503 miles). To the north, Benin is bordered by Burkina Faso (306 kilometers or 190 miles) and Niger (277 kilometers or 172 miles). These borders impact Benin’s cultural and economic interactions, with cross-border trade and cultural exchanges being significant aspects of life in border regions.
- Climate Influence on Geography: The varied climate of Benin, from the tropical conditions in the south to the more arid conditions in the north, plays a crucial role in shaping its geographical landscape. With more rainfall, the southern regions support lush vegetation and agricultural activities, while the north’s drier climate influences its more sparse vegetation and rugged terrain.
In summary, Benin’s geography, characterized by its mostly flat to undulating terrain, hills, low mountains, and a coastline along the Bight of Benin, presents a diverse ecological landscape. The country’s rivers, forests, and national parks add to its ecological richness. The shared borders with Togo, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, and Niger contribute to Benin’s cultural and economic dynamics. The geography of Benin, influenced by its varied climate, plays a vital role in the country’s agricultural practices, biodiversity, and overall way of life.
Resources and Land Use
Benin’s resources include small offshore oil deposits, limestone, marble, and timber. Agricultural land covers 31.3% of the country, with arable land constituting 22.9%. The nation’s forests account for 40% of the land area, highlighting the significance of forestry to the economy and environment.
Population Data
As of 2023, Benin has an estimated population of about 14.2 million. The population distribution is primarily concentrated in the south, with urban areas, particularly along the Atlantic coast, being more densely populated.
Economic Data
Benin’s economy is characterized by robust growth, with a GDP (PPP) of $43.17 billion in 2021. The nation’s main economic sectors include agriculture, industry, and services, with cotton being a significant export.
Drinking Water Source
In Benin, access to improved drinking water sources is at 74.7% of the population, with urban areas having slightly better access than rural regions.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Benin is 17.1 years, indicating a youthful population. The country experiences a small net migration rate of 0.2 migrants/1,000 population. Beninese citizenship is primarily based on descent, and dual citizenship is recognized.
Average Number of Childbirths
The average number of childbirths per woman in Benin is high, at 5.39 children born per woman (2023 est.), reflecting the nation’s youthful demographic and high fertility rate.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
While Benin is generally safe for travelers, it is advisable to remain cautious and informed about local conditions, especially given the regional challenges posed by terrorist groups in neighboring countries.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Benin’s healthcare system faces challenges, including a high maternal mortality ratio and a prevalence of infectious diseases like malaria and hepatitis A. Access to quality healthcare varies across the country.
Natural Hazards
The primary natural hazard in Benin is the hot, dry, dusty harmattan wind, which affects the north from December to March. This wind can significantly impact air quality and visibility.
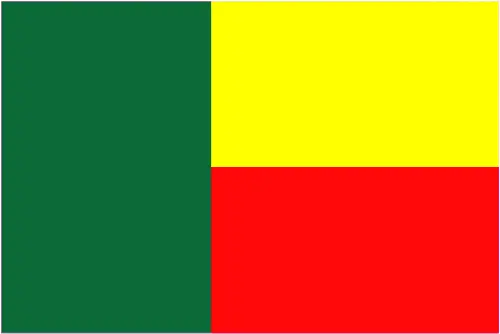
The Flag and Other Symbols
Benin’s flag consists of two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and red (bottom) with a vertical green band on the hoist side. These colors symbolize hope, wealth, and courage, respectively. The leopard is a national symbol representing strength and agility.
Constitution
Benin’s constitution, adopted in 1990, establishes a presidential republic with a multi-party system. It has undergone amendments to adapt to the evolving political landscape, including significant changes in 2019.
Legal System
The legal system in Benin is based on the French civil law system, integrated with some elements of customary law. The judiciary is independent, although challenges remain regarding resources and accessibility.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate in Benin is relatively low at 1.57% (2021 est.), but poverty remains widespread, with 38.5% of the population living below the poverty line as of 2019.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Benin’s fiscal policies focused on deficit reduction and management of debt, with public debt at 54.6% of GDP in 2017. The government aims to balance economic growth with fiscal responsibility.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in Benin was 1.73% in 2021, indicating a relatively stable price level. Information on the prime lending rate is not provided in the document.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Benin’s primary export partners include Nigeria, Bangladesh, and the United Arab Emirates, with major exports being gold, cotton, and cashews. Imports largely come from China, Thailand, and India, consisting of items like rice, cars, and palm oil.
Renewable Energies Used
Benin’s energy sector primarily depends on fossil fuels, with renewable energy sources like solar constituting only a small portion of its energy mix. Efforts are being made to increase the use of renewable energy.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Telecommunications in Benin is evolving, with mobile cellular subscriptions being predominant. The country code for Benin is +229.
Transport Infrastructure
Benin’s transport infrastructure includes roads, a few airports with paved runways, and waterways, primarily along the River Niger. The transport system plays a crucial role in economic activities and regional connectivity.
More Interesting Facts
Benin, a country with a rich cultural heritage and diverse natural landscapes, is full of fascinating facts many may not know. Here are some intriguing “Did you know” facts about Benin:
Did you know?
- Birthplace of Vodun (Voodoo): Did you know that Benin is considered the birthplace of Vodun, more commonly known as Voodoo? This traditional religion, which has significant spiritual and cultural importance, originated in this region of West Africa and was later spread to the Americas and the Caribbean through the transatlantic slave trade.
- The Dahomey Kingdom: Benin was once the center of the Dahomey Kingdom, a powerful West African empire that thrived from the 17th to the 19th century. The kingdom was known for its military prowess and wealth, and the Dahomey Amazons or Mino, an all-female military regiment that served as royal bodyguards and warriors.
- Unique Architecture of the Tata Somba: In northern Benin, you can find the Tata Somba, unique traditional two-story houses made of mud and straw. These houses, also found in neighboring Togo, symbolize the Somba people’s cultural identity and are noted for their distinct architectural style that blends living spaces with livestock quarters.
- Annual Voodoo Festival: Benin hosts an annual Voodoo Festival in January, attracting thousands of practitioners and curious visitors worldwide. This festival, held in Ouidah, a city with a significant history related to the slave trade, is a vibrant display of rituals, dances, and ceremonies.
- The Door of No Return: In Ouidah, the Door of No Return monument stands as a poignant reminder of the Atlantic slave trade. This archway, facing the ocean, symbolizes the final exit point of enslaved Africans leaving their homeland forever.
- Historical Kingdom of Abomey: The historical city of Abomey, once the capital of the Dahomey Kingdom, is famous for its royal palaces. These palaces, now a UNESCO World Heritage site, are a testament to the kingdom’s architectural and artistic achievements.
- Rich Biodiversity in Pendjari National Park: The Pendjari National Park, part of the larger W-Arly-Pendjari (WAP) complex, is one of West Africa’s most important wildlife reserves. It is home to various wildlife, including elephants, lions, and various antelope species, and is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Benin’s Role in the Songhai Empire: In the pre-colonial era, parts of northern Benin were under the influence of the Songhai Empire, one of the largest Islamic empires in history. This connection has left a lasting cultural and historical impact on the region.
These facts about Benin reveal a country with a deep historical legacy, rich cultural traditions, and diverse natural environments. From its historical kingdoms to its unique cultural practices and natural wonders, Benin remains a country with many layers of history and culture to explore.
Thank you for visiting and sharing this map & country information page.