Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Brazil (BR). This page lets you explore Brazil and its border countries (Country Location: Eastern South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Brazil and South America starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Brazil in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Brazil’s journey as a nation began over three centuries under Portuguese rule, culminating in its independence in 1822. The nation has experienced various forms of governance, from a monarchical system to periods of military rule, and now stands as a prominent democratic republic in South America.
Overview
Official Name: Federative Republic of Brazil
Date of Formation: September 7, 1822 (Independence from Portugal)
Capital: Brasília
Population: 218,689,757 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 8,515,770 sq km (land: 8,358,140 sq km, water: 157,630 sq km)
Population Density: 25.67 per sq. km
Languages: Portuguese (official), Spanish, German, Italian, Japanese, English, and a large number of minor Amerindian languages
Religions: Roman Catholic (50%), Evangelical (31%), Spiritist (3%), others
Ethnic Origin: White (47.7%), mixed (43.1%), Black (7.6%), Asian (1.1%), Indigenous (0.4%)
Government: Federal presidential republic
Currency: Real (BRL)
Literacy Rate: 94.3%
Calorie Consumption: N/A
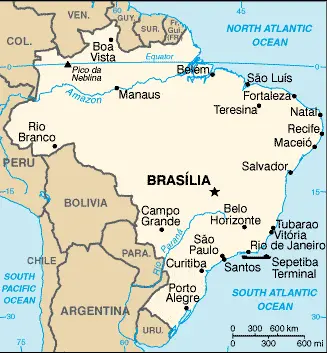
Brazil Google Maps
With its vast landscapes and diverse cultural heritage, Brazil is a captivating destination on Google Maps. Users can explore everything from the bustling streets of São Paulo to the Amazon rainforest, experiencing the country’s dynamic geography and vibrant urban centers.
Brazil is the world’s largest and most ecologically important rainforest, covering almost half of South America. The country has immense natural and economic resources. Rainforest grows around the massive Amazon River and its delta, covering almost half of Brazil’s total land area. Apart from the basin of the River Plate to the south, the rest of the country consists of highlands. The mountainous east is part-forested and part-desert. The coastal plain in the southeast has swampy areas. The Atlantic coastline is 1240 miles (2000 km) long.
The map below shows Brazil’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google map above shows Brazil with its location: South America (geographic coordinates: 10 00 S, 55 00 W) and the international borders of Brazil; total: 16,145 km. Border countries (total: 10): Argentina 1,263 km, Bolivia 3,403 km, Colombia 1,790 km, French Guiana 649 km, Guyana 1,308 km, Paraguay 1,371 km, Peru 2,659 km, Suriname 515 km, Uruguay 1,050 km, Venezuela 2,137 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Brazil and South America is for informational use only. No representation is made or warranted given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Brazil Google map and facts/wiki.
Climate
Brazil’s climate showcases fascinating diversity due to its vast size and varied topography. Here are some detailed insights into the country’s climatic conditions:
- Tropical North: The northern region of Brazil, which includes the Amazon Basin, experiences a tropical climate. This area is characterized by high temperatures and high humidity throughout the year. Average temperatures are consistently around 25°C to 28°C (77°F to 82°F). The Amazon Rainforest in this region is also known for its significant rainfall, especially during the wet season, which typically runs from November to May.
- Semi-Arid Northeast: The northeast of Brazil, particularly the interior, experiences a semi-arid climate. This region is much drier than the north, with some areas receiving less than 800 mm of rain annually. Periodic droughts can be a significant issue in this region, impacting agriculture and water supply.
- Temperate South: The southern part of Brazil, including states like Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, and Paraná, has a temperate climate with a more distinct four-season pattern. Winters can be quite cool, with occasional frost and snow in the higher altitude areas. Summer temperatures are warm but generally not as hot as in the tropical regions.
- Southeastern Variability: The southeastern region, including São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais, experiences a more variable climate. Coastal areas are typically warmer and more humid, while the highland areas can experience cooler temperatures. This region has a mix of tropical and subtropical climates.
- Central-West Climate: The Central-West region, home to the Pantanal wetlands, experiences a tropical wet and dry climate. The wet season here is typically from October to April, and the dry season is from May to September. The Pantanal, one of the world’s largest tropical wetland areas, is particularly affected by these seasonal changes.
- Rainfall Patterns: Brazil’s rainfall patterns are heavily influenced by factors like the Amazon Rainforest, the Andes Mountains, and ocean currents. The Amazon Rainforest is a significant driver of rainfall in Brazil and across South America.
- Climate Change Impacts: Brazil is experiencing various impacts due to climate change. These include changes in rainfall patterns, which affect both the Amazon Rainforest and agricultural regions, and rising temperatures, which affect ecosystems, water supply, and human health.
- Regional Climate Influencers: The El Niño and La Niña phenomena in the Pacific Ocean significantly impact Brazil’s climate. El Niño typically brings warmer and drier conditions, while La Niña can lead to cooler and wetter conditions.
- Urban Heat Islands: Major Brazilian cities like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro experience the urban heat island effect, where urban areas are significantly warmer than rural ones. This is due to high population density, concrete structures, and limited green space.
- Unique Microclimates: Brazil’s diverse topography, including mountains, plateaus, and coastal regions, creates unique microclimates. For example, the city of Petrópolis in the mountains of Rio de Janeiro state has a cooler climate. In contrast, the Fernando de Noronha archipelago has a tropical oceanic climate off the northeast coast.
Brazil’s climate is as varied as its landscape, ranging from the humid tropical regions in the north to the temperate zones in the south, each contributing to its rich tapestry of environmental experiences.
Geography
Brazil’s geography is diverse and fascinating, encompassing many natural landscapes and features. Let’s delve deeper into its geographical characteristics and neighboring countries:
- Vast Land Area: Brazil is the fifth-largest country in the world by land area, covering approximately 8.5 million square kilometers. This vast expanse contributes to its diverse landscapes and ecosystems.
- Northern Lowlands: The northern region of Brazil is dominated by the Amazon Basin, characterized by extensive flat and rolling terrain. This area is home to the largest tropical rainforest in the world, the Amazon Rainforest, which plays a crucial role in global biodiversity and climate regulation.
- Central Highlands: The Brazilian Highlands, or Planalto Brasileiro, are found in the central and southeastern parts of the country. This region is marked by rolling hills, plateaus, and some mountain ranges, with elevations generally between 300 and 2,000 meters. The highest point in Brazil, Pico da Neblina, stands at 2,994 meters and is near the Venezuelan border.
- Coastal Plains: A narrow coastal plain runs along the Atlantic Ocean. This region is characterized by beautiful beaches, coastal lagoons, and dune landscapes, contributing significantly to Brazil’s tourism industry.
- Major River Systems: Brazil’s river systems are extensive and complex. The Amazon River, the second-longest river in the world, is the most significant, with a basin that covers approximately 40% of South America. Other important rivers include the Paraná, the São Francisco, and the Tocantins.
- Pantanal Wetlands: Located primarily in Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, the Pantanal is one of the world’s largest tropical wetland areas. This region is renowned for its rich biodiversity and is a key area for wildlife and ecological conservation.
- Iguazu Falls: On the border with Argentina, the Iguazu Falls are among the world’s most spectacular waterfalls. They are located where the Iguazu River tumbles over the edge of the Paraná Plateau.
- Surrounding Countries:
- Argentina to the southwest,
- Bolivia and Peru to the west,
- Colombia to the northwest,
- Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana to the north,
- Paraguay and Uruguay to the south.
- Climatic Influence: Brazil’s vast geography means it experiences a wide range of climatic conditions, from the tropical climate in the Amazon to more temperate climates in the south.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Besides the Amazon Rainforest, Brazil hosts other biodiversity hotspots like the Atlantic Forest, the Cerrado, and the Caatinga, each with unique ecosystems and species.
- Natural Resources: Brazil is rich in natural resources, including vast reserves of iron ore, gold, diamonds, and oil. The Amazon rainforest is also a source of valuable timber and contains numerous medicinal plants and other unique biological resources.
Brazil’s geographical diversity, from the Amazon Rainforest to the Pantanal wetlands and the stunning Iguazu Falls, combined with its varied topography of lowlands, highlands, and coastal areas, make it one of the most geographically diverse countries in the world. This diversity is further enriched by its borders with numerous South American countries, each adding to the cultural and ecological richness of the region.
Resources and Land Use
The country is rich in natural resources like alumina, bauxite, gold, iron ore, and petroleum. Land use primarily focuses on agriculture (32.9%), with significant forest cover (61.9%), including the vast Amazon rainforest.
Population Data
Brazil’s population is concentrated along the Atlantic coast, especially in the southeast region, including major cities like São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Brasília. The population is diverse, with a mix of ethnicities and cultures.
Economic Data
As South America’s largest economy, Brazil has a varied industrial base, including automotive, mining, and energy sectors. The economy has faced challenges but is known for its resilience and potential for growth.
Drinking Water Source
Improved water sources are widely available, with urban access at 99.8% and rural at 96.9%. The vast river systems play a crucial role in supplying water.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Brazil is 34.7 years, reflecting a youthful but gradually aging population. Migration trends have varied over the years, with recent trends showing more Brazilians returning home from abroad.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Brazil stands at 1.75 children per woman, indicating a significant decline in birth rates over recent decades.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Brazil offers a diverse and vibrant cultural experience but is concerned with crime, particularly in urban areas. Travelers are advised to take standard safety precautions.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Brazil has an extensive public healthcare system, but access and quality challenges remain. Infectious diseases like dengue fever and malaria are present, especially in tropical regions.
Natural Hazards
Brazil faces natural hazards like droughts in the northeast and floods and occasional frosts in the south. The vast Amazon region is prone to environmental challenges related to deforestation and biodiversity loss.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Brazil’s flag, featuring a green field with a yellow diamond and a blue celestial globe with 27 white stars, symbolizes the country’s rich natural resources and diverse federal units.
Constitution
Brazil’s current constitution was ratified in 1988, marking a significant step in the country’s return to democratic governance. It outlines the federal structure and guarantees a range of civil liberties.
Legal System
Brazil follows a civil law system, which underwent significant reforms by enacting a new civil law code in 2002, replacing the 1916 code.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate stands at around 14.4%, reflecting economic challenges. While notable successes have been in reducing poverty, income inequality remains a significant issue.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Brazil’s public debt, standing at around 100.59% of GDP, is a matter of concern. Fiscal management remains a key focus for the government.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in Brazil is currently around 8.3%, which is high by international standards. The prime lending rate is adjusted in response to inflation and other economic indicators.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Brazil’s major export partners include China and the United States, with key exports like iron, soybeans, and crude petroleum. Imports are primarily from China and the U.S., including refined petroleum and vehicle parts.
Renewable Energies Used
Brazil is a leader in renewable energy, particularly in hydropower and bioenergy. The country’s energy matrix is one of the cleanest globally, with significant wind and solar energy investments.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Brazil has a robust telecommunications infrastructure, with many mobile cellular subscriptions and a growing broadband market. The country code is +55.
Transport Infrastructure
Brazil has a vast transport network, including the second largest number of airports globally and extensive roadways. The country also benefits from significant waterways for cargo and passenger transport.
More Interesting Facts
Brazil is renowned for its cultural diversity, vibrant festivals like Carnival, and the home of the Amazon rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest in the world. It is also famous for its contribution to football, having won the FIFA World Cup a record five times.
Did You Know?
- Fifth-Largest Country: Brazil is the fifth-largest country in the world by land area and population. Its vast size covers a range of ecosystems and climates, making it one of the most biodiverse countries on Earth.
- Amazon Rainforest: Approximately 60% of the Amazon Rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest in the world, is located in Brazil. This rainforest is home to about one-tenth of all species worldwide and is crucial in regulating the Earth’s oxygen and carbon cycles.
- River by Volume: The Amazon River, flowing through Brazil, is not the longest river in the world (that title goes to the Nile), but it is the largest by volume. It discharges about 209,000 cubic meters per second, more than the next seven largest independent rivers combined.
- Unique Wildlife: Brazil boasts an incredible array of wildlife, much of which is unique to the country. It’s home to diverse species like jaguars, macaws, capybaras, and the Amazon river dolphin, the world’s largest species of freshwater dolphin.
- Pantanal: The world’s largest tropical wetland area, the Pantanal, is primarily located in Brazil. This region has the highest concentration of wildlife in South America, including a dense population of jaguars.
- Coffee Production: Brazil is the world’s largest producer of coffee, a title it has held for over 150 years. It produces about a third of the world’s coffee supply.
- Cultural Diversity: Brazil’s population is one of the most ethnically diverse in the world, resulting from centuries of immigration. It’s particularly noted for its Portuguese, African, Indigenous, Italian, German, Spanish, and Japanese communities.
- Carnival: The Brazilian Carnival, particularly the one held in Rio de Janeiro, is one of the most famous cultural celebrations globally, attracting millions of tourists every year with its vibrant parades, music, and dance.
- Iguazu Falls: The Iguazu Falls, located on the border of Brazil and Argentina, are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. They are taller and twice as wide as Niagara Falls, consisting of approximately 275 individual waterfalls.
- Christ the Redeemer: One of Brazil’s most iconic landmarks is the Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro. Standing 30 meters tall atop Corcovado Mountain, it is one of the World’s New Seven Wonders.
- Unique Sports Achievements: Brazil is the only country to have participated in every FIFA World Cup since the tournament’s inception in 1930 and the only nation to have won the World Cup five times.
- Biodiversity: Brazil is a megadiverse country, home to a wide range of unique ecosystems, including the Amazon Rainforest, the Atlantic Forest, the Cerrado, the Pantanal, and the Caatinga, each with its distinct ecological characteristics and species.
These facts about Brazil highlight its immense geographical, biological, cultural, and social diversity, making it a unique and fascinating country on the global stage.
Thank you for visiting and sharing this map & country information page.