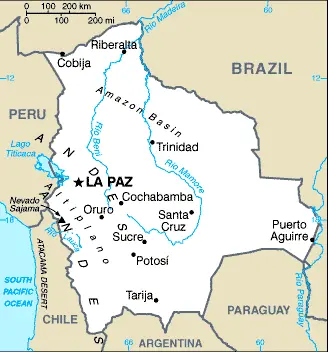
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Bolivia (BO). This page lets you explore Bolivia and its border countries (Country Location: Central South America, southwest of Brazil) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Bolivia, in South America, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Bolivia in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
In honor of Simon Bolivar, Bolivia gained independence from Spanish rule in 1825. Numerous coups mark its history, the last in 1978, before democratic civilian rule was established in 1982. Despite this, Bolivia’s leaders have continuously grappled with challenges like deep-seated poverty, social unrest, and the production of illegal drugs. Evo Morales, elected in 2005, aimed to transform the political class and empower the nation’s poor and indigenous majority. His presidency saw multiple re-elections until allegations of electoral fraud in 2019 led to his resignation. Luis Alberto Arce Catacora was elected president in 2020 following an interim government.
Overview
Bolivia, a South American country southwest of Brazil, is renowned for its diverse terrain spanning the Andes Mountains, the Atacama Desert, and the Amazon Basin rainforest. It’s a landlocked nation but rich in natural resources like lithium, tin, and natural gas. Bolivia’s vibrant cultural tapestry reflects the legacy of its indigenous peoples and colonial history.
Official Name: Plurinational State of Bolivia
Date of Formation: 6 August 1825 (from Spain)
Capital: La Paz (administrative capital); Sucre (constitutional capital)
Population: 12,186,079 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 1,098,581 sq km
Population Density: 11.1 people per sq km (based on 2023 population and total area)
Languages: Spanish (official) 68.1%, Quechua (official) 17.2%, Aymara (official) 10.5%, Guarani (official) 0.6%, other 1.5%, unspecified 2.1% (2012 estimate)
Religions: Roman Catholic 70%, Evangelical 14.5%, Adventist 2.5%, Church of Jesus Christ 1.2%, agnostic 0.3%, atheist 0.8%, other 3.5%, none 6.6%, unspecified 0.6% (2018 estimate)
Ethnic Origin: Mestizo (mixed White and Amerindian ancestry) 68%, Indigenous 20%, White 5%, Cholo/Chola 2%, African descent 1%, other 1%, unspecified 3% (2009 estimate)
Government: Presidential republic
Currency: Bolivianos (BOB)
Literacy Rate: Total population: 92.5%, Male: 96.5%, Female: 88.6% (2015)
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Bolivia Google Maps
Google Maps offers detailed views of Bolivia’s varied landscapes, from the sprawling Altiplano to the dense Amazonian jungles. The service is invaluable for navigating Bolivia’s major cities like La Paz and Santa Cruz and exploring its natural wonders and historical sites.
Landlocked high in central South America, Bolivia is one of the region’s poorest countries. La Paz is the world’s highest capital city: 13,385 feet (3631 m) above sea level. A high windswept plateau, the Altiplano, lies between two Andean mountain ranges. Semiarid grasslands to the east; dense tropical forests to the north.
The map below shows Bolivia’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google map above shows Bolivia with its location: South America (geographic coordinates: 17 00 S, 65 00 W) and the international borders of Bolivia; total: 7,252 km. Border countries (total: 5): Argentina 942 km, Brazil 3,403 km, Chile 942 km, Paraguay 753 km, Peru 1,212 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Bolivia, South America, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Bolivia Google map and facts/wiki.
Climate
Bolivia’s climate is as diverse as its terrain, largely due to the dramatic variations in altitude across the country. From steamy Amazonian lowlands to the frigid heights of the Andes, Bolivia’s climatic conditions are a study in contrasts.
- Variation with Altitude: Altitude is Bolivia’s most significant climate factor. The lowlands’ climate is humid and tropical, particularly in the Amazon basin. Here, temperatures average around 30°C (86°F), with high humidity levels and significant rainfall, especially during the rainy season from November to March.
- Highland Climate: As you ascend to the highlands, including the Altiplano region and cities like La Paz and Potosí, the climate becomes markedly colder and semiarid. The Altiplano region experiences significant diurnal temperature variations, where daytime temperatures might reach 20°C (68°F), dropping to near or below freezing at night. The dry season in these highlands spans from May to October and is characterized by clear, sunny days and cold nights.
- Influence of the Andes: The Andes Mountains are crucial in Bolivia’s weather patterns. They act as a barrier, trapping moisture in the lowlands and creating a rain shadow effect in the highlands. This geographical feature results in distinct microclimates within the country. For example, the Yungas, a narrow band of forest along the eastern slopes of the Andes, receives heavy rainfall and has a subtropical climate, contrasting sharply with the arid Altiplano just kilometers away.
- Seasonal Variations: Bolivia experiences two main seasons – the wet season and the dry season. From November to March, the wet season sees the most annual rainfall, especially in the lowlands and the Yungas region. From April to October, the dry season is characterized by drier conditions, which can be particularly harsh in the highlands, leading to cold temperatures and frost.
- Extreme Weather Events: Bolivia is also subject to various extreme weather events influenced by its diverse climate. These include heavy rains and flooding in the lowlands and severe droughts in the highlands. In recent years, the effects of climate change have begun to alter traditional weather patterns, exacerbating these extreme events.
- Agricultural Impacts: The varied climate greatly influences agricultural practices across Bolivia. The tropical lowlands are suitable for crops like soybeans, sugarcane, and rice, while potatoes, quinoa, and other tubers are commonly grown in the cooler highlands. The diversity of microclimates also allows for cultivating a wide range of fruits and vegetables throughout the country.
Its varied topography deeply influences Bolivia’s climate, particularly the altitude. From tropical conditions in the lowlands to colder, semiarid conditions in the highlands, the country’s diverse climate affects its ecosystems, agriculture, and the day-to-day lives of its people. The Andes Mountains are a key factor in creating these varied conditions, leading to many microclimates within a relatively small geographical area.
Geography
Bolivia’s geography, spanning central South America at geographic coordinates of 17°00’S and 65°00’W, presents a diverse and complex landscape. With an area of approximately 1,098,581 square kilometers (424,164 square miles), it is slightly less than three times the size of Montana, offering a rich tapestry of geographic features.
- Diverse Landforms: The country’s topography is characterized by three distinct regions: the rugged Andes Mountains, the highland plateau known as the Altiplano, and the lowland plains of the Amazon Basin. Each region has its unique geographic features and ecosystems.
- The Andes Mountains: To the west, the Andean region is marked by two major mountain ranges that run parallel to each other. This region is home to some of the highest peaks in the Western Hemisphere, including Nevado Sajama, which reaches 6,542 meters (21,463 feet) above sea level. The Andes are a defining feature of Bolivia’s landscape and influence its climate and water resources.
- The Altiplano: Between these mountain ranges lies the Altiplano, a vast highland plateau at an average elevation of about 3,650 meters (11,975 feet). This area includes Lake Titicaca, the world’s highest navigable lake, shared with Peru, and the Uyuni Salt Flats, the largest salt flat in the world, a significant tourist attraction and a vital source of lithium.
- Amazon Basin: To the north and east, the terrain descends into the lowland plains of the Amazon Basin. This region is covered by dense rainforest and includes parts of the Amazon River system. It boasts a rich biodiversity and is crucial for the country’s agriculture, especially in cultivating soybeans and other crops.
- Surrounding Countries: Bolivia is landlocked, sharing borders with five countries. To the north and east, it borders Brazil, with a boundary of about 3,423 kilometers (2,126 miles). To the south, it shares borders with Paraguay (753 kilometers or 468 miles) and Argentina (942 kilometers or 585 miles). Chile lies to the southwest (942 kilometers or 585 miles), and Peru to the northwest (1,075 kilometers or 668 miles). These borders influence Bolivia’s cultural and economic interactions.
- Natural Resources: Bolivia’s diverse geography endows it with abundant natural resources. The country is rich in silver, gold, tin, and lithium minerals. The lowland regions are fertile and support agriculture, while the Andean region is home to extensive mineral deposits.
- Environmental Challenges: Bolivia faces various environmental challenges, including deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution. The impact of climate change is particularly evident in the melting of Andean glaciers, affecting water supply for both agricultural and human consumption.
In summary, Bolivia’s geography is marked by its vast, diverse landscapes, from the high peaks of the Andes and the expansive Altiplano to the lush lowlands of the Amazon Basin. This diverse topography not only shapes the country’s ecosystems and climate but also influences its cultural identity and economic activities. Bolivia’s position as a landlocked nation surrounded by five countries adds to its strategic and cultural significance in South America.
Resources and Land Use
Bolivia has abundant natural resources, including lithium, tin, natural gas, and petroleum. About 34.3% of its land is used for agriculture, with forests covering 52.5%. Irrigated land encompasses approximately 2,972 sq km.
Population Data
As of 2023, Bolivia’s population is approximately 12.18 million, ranking 79th globally. The country has a diverse ethnic composition with a significant indigenous presence.
Economic Data
Bolivia’s economy is varied, with key sectors including mining, natural gas, and agriculture. The GDP is about $97.26 billion as of 2021, with a growth rate of 6.11%. The country faces challenges such as income inequality and poverty.
Drinking Water Source
In Bolivia, 93.5% of the population has access to improved water sources. Urban areas have higher access rates (99.2%) than rural areas (80.2%).
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Bolivia is 26.2 years. Migration has been a significant factor, with a net migration rate -1 per 1,000 population. The country experiences a mix of emigration and immigration, influenced by economic factors.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Bolivia is 2.26 children per woman as of 2023, reflecting a moderate birth rate.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
While Bolivia offers rich cultural experiences and natural beauty, safety concerns such as petty crime and political unrest are present. Travelers are advised to exercise caution and stay informed about local conditions.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
The healthcare system in Bolivia is evolving, with ongoing challenges in rural areas. Infectious diseases like dengue fever and malaria are prevalent. The country has a physician density of 1.03 per 1,000 population.
Natural Hazards
Bolivia faces natural hazards like flooding, particularly in the northeast, and volcanic activity in the Andes.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The Bolivian flag features three horizontal bands of red, yellow, and green, symbolizing bravery, mineral resources, and land fertility. The coat of arms is centered on the yellow band. Bolivia also recognizes the llama, the Andean condor, and two national flowers, the cantuta, and the patuju, as national symbols.
Constitution
Bolivia’s current constitution was adopted in 2009, reflecting significant changes in its governance and recognition of its indigenous peoples.
Legal System
The Bolivian legal system is based on a civil law system influenced by Roman, Spanish, canon, French, and indigenous law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate in Bolivia was 8.51% as of 2021, with significant underemployment. The country struggles with a high poverty rate, with 37.2% of the population living below the poverty line as of 2019.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Bolivia’s public debt was 49% of its GDP in 2017, with government revenues at 39.9% of GDP.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in Bolivia was relatively low at 0.74% in 2021. The prime lending rate reflects the country’s economic policies and market conditions.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Bolivia’s main export partners include Argentina, Brazil, and the United Arab Emirates, with key exports being gold, natural gas, and zinc. Its imports, including cars and refined petroleum, predominantly come from Brazil and Chile.
Renewable Energies Used
Bolivia is increasingly investing in renewable energy sources, with hydroelectricity accounting for 30.5% of its total installed capacity as of 2020.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
The country’s telecommunications infrastructure is rapidly evolving, focusing on mobile and broadband services. Bolivia’s country code is +591.
Transport Infrastructure
Bolivia’s transport infrastructure includes extensive roadways, railways, and many airports. The country has made strides in improving connectivity, particularly in remote areas.
More Interesting Facts
Bolivia, a country with a rich cultural heritage and diverse natural landscapes, is full of surprising and unique facts. Here are some interesting “Did you know” tidbits about Bolivia:
Did you know?
- The Highest Administrative Capital: Did you know that La Paz, the administrative capital of Bolivia, is the highest in the world? It sits at an elevation of roughly 3,650 meters (11,975 feet) above sea level.
- Largest Salt Flat: Bolivia is home to Salar de Uyuni, the world’s largest salt flat, spanning an area of over 10,000 square kilometers (3,860 square miles). This vast white expanse is especially stunning after a rain when it becomes a giant mirror reflecting the sky.
- Diverse Indigenous Cultures: Bolivia has one of the highest percentages of Indigenous peoples in South America. Over 60% of its population identifies as Indigenous, belonging to various ethnic groups, including the Quechua and Aymara.
- A Landlocked Nation: Bolivia became a landlocked country following the War of the Pacific (1879-1883), in which it lost its coastal territory to Chile. This has significantly influenced its history and economic development.
- A Country of Many Official Languages: While Spanish is widely spoken, Bolivia recognizes 36 official languages, including various Indigenous languages. This reflects the country’s rich cultural and linguistic diversity.
- The Birthplace of the Inca Empire: According to some historians, the Inca Empire originated in the Lake Titicaca region, part of which lies in modern-day Bolivia. The ruins of Tiwanaku, near the lake, testify to an advanced pre-Inca civilization.
- The Death of Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid: Bolivia is believed to be where the notorious American outlaws Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid met their end. They reportedly were killed in a shootout in the small town of San Vicente.
- Unique Wildlife in Madidi National Park: Madidi National Park in the Bolivian Amazon is one of the most biodiverse places on Earth. It hosts over 11% of the world’s bird species and many other wildlife.
- Bolivia’s Witch Market: In La Paz’s famous Witch Market, or Mercado de las Brujas, one can find an array of traditional Andean remedies and spiritual items, including dried llama fetuses used in local Aymara rituals.
- Traditional Bolivian Music: Bolivia has a rich folk music tradition, with instruments like the charango (a small Andean guitar) and panpipes being widely used. These traditional sounds are an integral part of Bolivian cultural celebrations and festivals.
These facts about Bolivia highlight the country’s intriguing blend of cultural richness, historical significance, and natural wonders. From its high-altitude cities to the expansive salt flats and deep indigenous roots, Bolivia is a country that continually captivates and surprises.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!