Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Antigua and Barbuda (AG). This page lets you explore Antigua and Barbuda and its border countries (Country Location: the Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Antigua and Barbuda, Central America, and the Caribbean starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
Borderline map of Antigua and Barbuda
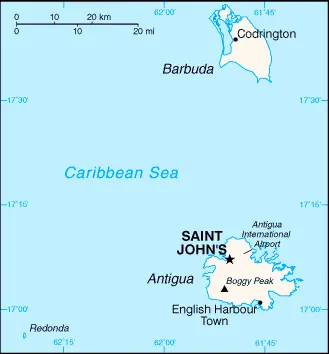
Location map of Antigua and Barbuda
Flag of Antigua and Barbuda

Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Antigua and Barbuda’s history dates back to the first inhabitants, the Siboney, around 2400 B.C. The Arawak Indians populated the islands when Christopher Columbus landed in 1493. Early Spanish and French settlements were succeeded by an English colony in 1667. The islands played a significant role in the sugar plantation economy, with slavery abolished in 1834. Gaining independence from the British Commonwealth in 1981, the nation has since developed a strong tourism-driven economy. In 2017, Hurricane Irma severely damaged Barbuda, leading to the evacuation of the population to Antigua.
Overview
Antigua and Barbuda, a twin-island nation in the Caribbean, is renowned for its reef-lined beaches, lush landscapes, and vibrant culture. The nation’s economy primarily revolves around tourism, followed by the construction sector and light manufacturing. As an independent state, it is a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy, being part of the Commonwealth realm.
Official Name: Antigua and Barbuda
Date of Formation: Became independent in 1981
Capital: Saint John’s
Population: Approximately 101,489 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 443 square kilometers (Antigua 280 sq km; Barbuda 161 sq km; includes Redonda, 1.6 sq km)
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English (official)
Religions: Predominantly Christian
Ethnic Origin: Predominantly of African descent
Government: Parliamentary Democracy under Constitutional Monarchy
Currency: East Caribbean Dollar (XCD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Antigua and Barbuda Google Maps
Located in the Caribbean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico, Antigua and Barbuda’s geographic beauty and key locations are accessible via Google Maps. This tool is beneficial for exploring the islands’ natural harbors, beaches, and landmarks.
The map below shows Antigua and Barbuda with their cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google map above shows Antigua and Barbuda with its location: Central America and the Caribbean (geographic coordinates: 17 03 N, 61 48 W) and Antigua and Barbuda; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The map of Antigua and Barbuda, Central America, and the Caribbean is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Antigua and Barbuda Google map and facts/wiki.
Climate
The islands referred to in your query are not specified, but many island nations and territories in tropical regions share similar climatic characteristics. Assuming a general tropical maritime climate, here’s an extended overview of such conditions, which are typical for islands in the Caribbean, parts of Southeast Asia, the South Pacific, and similar regions:
- Stable Temperatures: Tropical maritime climates are characterized by stable, warm temperatures throughout the year. The average temperature typically ranges from about 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F). These consistently warm conditions are a key factor in the appeal of these islands as year-round tourist destinations.
- High Humidity: Humidity levels in tropical maritime climates are generally high, often exceeding 75%. This high humidity can make the heat feel more intense, but it also contributes to the lush, green landscapes and rich biodiversity of these islands.
- Rainfall Patterns: While there is little seasonal temperature variation, there are distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, often coinciding with the summer months, sees the majority of the year’s rainfall. Rainfall during this period can be heavy but is usually short-lived, often occurring in the late afternoon or evening.
- Hurricane or Cyclone Season: Many islands with a tropical maritime climate, especially those in the Caribbean and the South Pacific, experience a hurricane or cyclone season. This season typically runs from June to November in the Caribbean and from November to April in the South Pacific. While not all islands are affected every year, the possibility of tropical storms or hurricanes is a significant aspect of the climate.
- Moderating Effect of the Sea: The proximity to the sea helps moderate temperature extremes on these islands. Sea breezes have a cooling effect, particularly along the coast, making the climate more comfortable compared to inland areas at similar latitudes.
- Sunshine Hours: Tropical maritime islands typically enjoy ample sunshine year-round, contributing to their popularity as tourist destinations. Even during the wet season, sunny days or parts of days are common.
- Impact on Ecosystems: The warm, humid climate supports diverse ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs. These ecosystems are not only vital for wildlife but also attract ecotourism.
- Variability with Elevation: On islands with mountainous terrain, the climate can vary with elevation. Higher elevations may experience cooler temperatures and more rainfall, supporting different types of vegetation and offering a respite from the heat of lower areas.
- Climate Change Impacts: These islands are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Rising sea levels, increased intensity of tropical storms, and changes in rainfall patterns pose significant risks to their environments, economies, and populations.
- Cultural and Economic Importance: The climate is integral to the culture and economy of these islands, particularly regarding tourism, agriculture, and fishing. Festivals, outdoor activities, and agriculture practices are often closely tied to the seasonal climate patterns.
The tropical maritime climate of these islands, with its warm temperatures, high humidity, and distinct wet and dry seasons, plays a crucial role in shaping their natural beauty, biodiversity, and way of life. Understanding these climatic conditions is essential for sustainable development, especially in the context of tourism and environmental conservation.
Geography
Antigua and Barbuda’s geography, characterized by its combination of low-lying limestone and coral formations along with higher volcanic areas, shapes the twin-island nation’s landscape and influences its natural environment. Here’s an extended overview of Antigua and Barbuda’s geographical features, including more detailed statistics and information about its surrounding regions:
- Island Composition: The nation comprises two main inhabited islands, Antigua and Barbuda, and several smaller islands, including the uninhabited island of Redonda. Antigua is the larger and more populous of the two main islands.
- Topography: While much of Antigua and Barbuda is low-lying, with beaches and coastal plains, there are some elevated areas. The islands are primarily composed of limestone and coral, but Antigua also has volcanic areas, which contribute to its more varied topography.
- Highest Point – Mount Obama: Formerly known as Boggy Peak, Mount Obama is the highest point in Antigua and Barbuda, standing at 402 meters (1,319 feet). It is located in the southwestern part of Antigua and offers panoramic views of the island.
- Lowest Point: The lowest point in Antigua and Barbuda is at sea level along the Caribbean Sea. The nation’s coastline is characterized by numerous beaches, bays, and natural harbors.
- Total Area: The combined land area of Antigua and Barbuda is about 443 square kilometers (171 square miles). Antigua itself accounts for the majority of this area, measuring about 281 square kilometers (108 square miles), while Barbuda covers about 161 square kilometers (62 square miles). Redonda, the smallest of the main islands, is about 1.6 square kilometers (0.6 square miles).
- Coastline: Antigua and Barbuda have a relatively long coastline for their size, with numerous beaches that are popular tourist destinations. The coastline features a mix of sandy beaches and rocky shores, with coral reefs offshore.
- Climate Influence: The geographical location of Antigua and Barbuda in the eastern Caribbean influences its tropical maritime climate. The islands experience warm temperatures year-round, moderated by northeast trade winds.
- Surrounding Waters: The nation is surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. These surrounding waters play a crucial role in the islands’ climate, economy (especially tourism and fishing), and biodiversity.
- Surrounding Countries: The closest neighboring countries to Antigua and Barbuda are Saint Kitts and Nevis to the west, Montserrat to the southwest, and Guadeloupe to the south. These neighboring islands are part of the Lesser Antilles island chain in the Caribbean.
- Environmental Challenges: Like many Caribbean nations, Antigua and Barbuda face environmental challenges related to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, and the impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise and coral reef degradation.
Antigua and Barbuda’s geography, with its beautiful beaches, coral reefs, and volcanic landscapes, not only defines its natural beauty but also influences its culture, economy, and environmental considerations. The nation’s position in the Caribbean and its relationship with nearby islands are important for understanding its role in the region.
Resources and Land Use
The nation’s natural resources are negligible; however, the pleasant climate fosters tourism, which is the mainstay of the economy.
Population Data
As of 2023, the population is estimated at 101,489. The island of Antigua houses approximately 97% of the population, with most of Barbuda’s population residing in Codrington.
Economic Data
The real GDP was $1.783 billion in 2021, with a growth rate of 5.27%. The nation’s economy is driven by tourism, construction, and light manufacturing.
Drinking Water Source
About 96.7% of the population has access to improved drinking water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Antigua and Barbuda is 33.6 years. The net migration rate is 2 migrants/1,000 population (2023 estimate).
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate is 1.94 children born per woman (2023 estimate).
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Antigua and Barbuda is generally considered a safe destination with a low crime rate, making it popular among tourists.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
The current health expenditure is 5.6% of GDP (2020), with a physician density of 2.76 physicians/1,000 population (2017).
Natural Hazards
The islands are prone to hurricanes and tropical storms, particularly from July to October, and periodic droughts.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The flag features red, with an inverted isosceles triangle based on the top edge; it contains three horizontal bands of black, light blue, and white, with a yellow rising sun in the black band.
Constitution
The current constitution was presented in 1981, marking the nation’s independence. It has undergone several amendments, the latest in 2018.
Legal System
The legal system is based on English common law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate was 11% in 2014. Data on the poverty line is not specified.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The budget revenues were $278 million against expenditures of $357 million in 2020. Public debt stood at 86.8% of GDP in 2017.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate was 2.06% in 2021.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Major exports include refined petroleum, ships, and gas turbines. Key import partners are the United States, Poland, and China.
Renewable Energies Used
Information on renewable energies used in Antigua and Barbuda is not specified.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Telecommunications in Antigua and Barbuda are developing, with a country code of +1-268.
Transport Infrastructure
Transportation infrastructure includes three airports and major seaports in Saint John’s and a cruise port in St. John’s.
More Interesting Facts
Antigua and Barbuda is famous for its 365 beaches, one for each day of the year, its vibrant cultural festivals like Carnival, and as a haven for yachting and sailing.
Did You Know?
- Land of 365 Beaches: Antigua is often touted as the land of 365 beaches, one for each day of the year. These beaches are known for their stunning beauty, with white sand and crystal-clear turquoise waters.
- Historical Significance of Nelson’s Dockyard: Nelson’s Dockyard in Antigua, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the only continuously operating Georgian dockyard in the world. It was once used by the British Royal Navy and is named after Admiral Horatio Nelson, who lived in Antigua in the 1780s.
- Highest Point Named After a U.S. President: The highest point in Antigua, formerly known as Boggy Peak, was renamed Mount Obama on August 4, 2009, in honor of Barack Obama, the first African-American President of the United States.
- A Haven for Sailing: Antigua is renowned for its sailing and yachting events. The annual Antigua Sailing Week, one of the premier sailing regattas in the world, attracts sailors and spectators from around the globe.
- Bird Sanctuary in Barbuda: The Frigate Bird Sanctuary in Barbuda is one of the largest in the Western Hemisphere. It is home to over 5,000 frigate birds and is accessible only by boat.
- Unique Pink Sand Beaches: Barbuda is known for its pink sand beaches, a rare and stunning natural phenomenon. The pink hue comes from tiny crushed coral pieces mixed with the sand.
- Cultural Blend: The culture of Antigua and Barbuda is a vibrant mix of West African, British, and Creole influences, reflected in the nation’s music, dance, and cuisine.
- Historical Sugar Production: In the 17th and 18th centuries, Antigua was an important sugar-producing colony, dotted with numerous sugar plantations and mills. The remnants of these plantations are still visible across the island.
- Independence from Britain: Antigua and Barbuda became an independent state within the Commonwealth of Nations on November 1, 1981. Before this, it was under British rule for several centuries.
- National Dish: The national dish of Antigua and Barbuda is fungie (pronounced “foon-jee”) and pepperpot. Fungie is a cornmeal dish similar to Italian polenta, and pepperpot is a hearty stew made with vegetables and various meats.
- Carnival Celebration: The Antigua Carnival, held annually at the end of July and into August, is a colorful and festive celebration filled with music, dance, parades, and costumes, marking the island’s emancipation from slavery in 1834.
- Redonda – A Unique Part of the Nation: The uninhabited island of Redonda, part of Antigua and Barbuda, has a unique history with quirky tales of being a kingdom and is known for its seabird colonies and rare flora and fauna.
These facts about Antigua and Barbuda highlight the country’s rich history, stunning natural beauty, and vibrant culture, making it a fascinating destination in the Caribbean.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!
